What is Point Cloud?
In the world of 3D technology, the term “point cloud” has gained traction. A point cloud is a collection of data points in a three-dimensional space that meticulously captures the external surface of an object or environment. This article takes us deep into the fascinating world of point clouds, exploring their creation, applications, and impact on various industries.
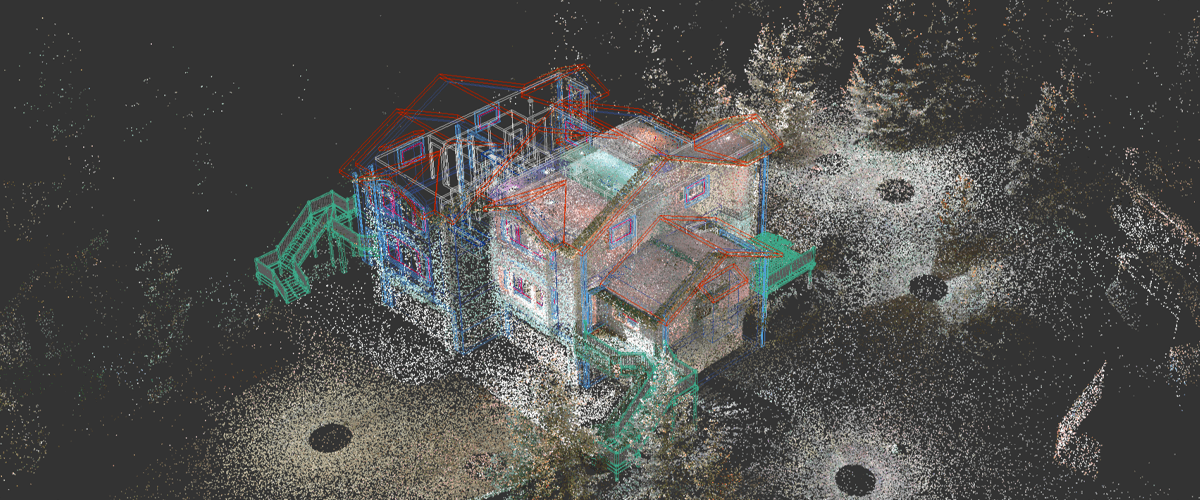
How Are Point Clouds Generated?
Point clouds come to life through advanced 3D scanning technologies, with LiDAR being a primary player. LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) employs laser beams to measure the time it takes for light to return after hitting an object. This process creates a detailed point cloud by capturing spatial coordinates (X, Y, and Z) for each point.
How Do Point Clouds work?
Each point in the cloud represents a specific location in the three-dimensional coordinate system. Together, these points form a detailed representation of the object or environment, offering a wealth of information about its shape and structure.
What Applications do Point Clouds have?
1. 3D Modeling:
Point clouds serve as the foundation for creating intricate 3D models. Whether in architecture, product design, or entertainment, this application allows for the accurate representation of physical objects in the digital realm.
2. Augmented and Virtual Reality:
In the realms of AR and VR, point clouds elevate user experiences by providing realistic and immersive environments. The precision of point cloud data enhances the authenticity of virtual worlds and augmented overlays.
3. Surveying and Mapping:
For professionals in fields like construction, topography, land surveying, and urban planning, point clouds generated through LiDAR technology offer a precise and efficient way to map and analyze landscapes.
4. Reverse Engineering:
Point clouds play a crucial role in reverse engineering, enabling the recreation of digital models based on existing physical objects. This application is invaluable in design and manufacturing processes.
5. Object Recognition:
In computer vision, point clouds are analyzed to identify and recognize objects within a scene. This application is fundamental for various industries, including robotics and automation.
6. Autonomous Vehicles:
LiDAR sensors on autonomous vehicles leverage point clouds to perceive and navigate the surrounding environment. This technology is vital for ensuring the safety and efficiency of self-driving vehicles.
How Do You Process and Analyze Point Clouds?
Working with point clouds goes beyond simple data collection. It involves sophisticated processes to extract meaningful information. Tasks such as noise filtering, object segmentation, and surface reconstruction are essential for making sense of the vast amount of data captured by point clouds.
Summarizing, point clouds represent a groundbreaking technology with applications spanning a multitude of industries. From revolutionizing 3D modeling and enhancing virtual experiences to aiding in urban planning and autonomous vehicle navigation, the impact of point clouds is profound. As technology continues to advance, point clouds will likely play an increasingly pivotal role in shaping the future of 3D applications and innovations.
