LiDAR, which stands for Light Detection and Ranging, is a remote sensing method that uses light in the form of a pulsed laser to measure variable distances. Essentially, it works by sending out laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for the light to return after bouncing off objects in its path. This data is then used to create precise 3D maps or models of the surveyed area.
LiDAR and it’s relevance across various fields:
- AEC: After completion, 3D scans provide comprehensive as-built documentation. This helps in facility management, future renovations, and serves as a valuable reference for any modifications or expansions.

- Multifamily and Property Developers: Property developers can use 3D scanning to create immersive virtual tours of properties. This allows potential buyers or renters to explore the spaces remotely, saving time and resources for both parties. Also, 3D scans serve as valuable historical documentation for properties. They capture the state of the property at a specific time, which can be useful for future renovations, insurance purposes, or legal documentation.
- Insurance Industry and Restoration Contractors: 3D Scans provide detailed and precise information and data on damaged properties, enabling restoration contractors and adjusters to assess the extent of damage more accurately. This facilitates better planning and estimation of restoration efforts and cost.
- Heritage Sites and Museums: Generate precise and detailed 3D models of the museum or heritage site, ensuring accuracy in spatial representation. This benefit is crucial for architects, curators, and educators to visualize and analyze the space, facilitating informed decision-making, and contributing to the overall preservation and planning efforts.
- Mapping and Surveying: LiDAR is extensively used in cartography, forestry, urban planning, and archaeology for creating highly accurate digital elevation models, contour maps, and terrain models.
- Infrastructure Management: LiDAR is used for monitoring infrastructure such as bridges, dams, and pipelines for signs of wear and tear, deformation, or damage. It helps in predictive maintenance and ensuring the safety and longevity of critical infrastructure.
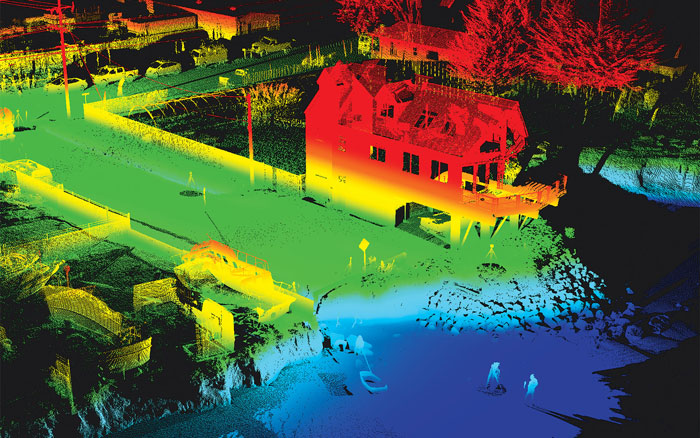

- Disaster Management: LiDAR data can aid in disaster management by providing detailed information about terrain and infrastructure, helping responders assess damage, plan rescue operations, and mitigate future risks.
- Autonomous Vehicles: LiDAR is a crucial technology for autonomous vehicles (AVs) as it helps them detect and navigate obstacles and understand their surroundings in real-time. AVs use LiDAR to create detailed 3D maps of their environment, allowing them to make informed decisions about navigation and avoiding collisions.
- Urban Development: LiDAR assists urban planners in understanding urban morphology, analyzing land use patterns, and managing urban growth effectively. It enables the creation of detailed models for simulating and visualizing urban development scenarios.
Overall, LiDAR technology plays a significant role in various industries and has diverse applications that range from mapping and navigation to environmental monitoring and infrastructure management. As it continues to evolve and become more accessible, its relevance and impact are expected to grow even further.
